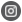
The crankshaft sensor, often referred to as the crankshaft position sensor, is a crucial component in modern vehicle engines. It monitors the position or rotational speed of the crankshaft and sends this information to the engine control unit (ECU). The ECU uses this data to manage ignition timing, fuel injection, and other essential engine functions to optimize performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown of the crankshaft sensor:
-
Function: The primary function of the crankshaft sensor is to detect the position and speed of the crankshaft, which is crucial for the proper timing of the engine’s ignition and fuel injection. It ensures that the engine operates smoothly and efficiently.
-
Types of Sensors: Crankshaft sensors come in two common types:
- Magnetic sensors: These work by detecting the magnetic field changes caused by the teeth of a reluctor wheel attached to the crankshaft.
- Hall effect sensors: These generate electrical signals when a magnet in the sensor interacts with the rotating crankshaft.
-
Symptoms of Failure: If the crankshaft sensor fails, the engine may fail to start, experience rough idling, misfires, or exhibit poor acceleration. The vehicle may also trigger a check engine light.
-
Location: Typically, the crankshaft sensor is located near the crankshaft, often near the timing gear or the flywheel, but this varies depending on the vehicle model.
-
Replacement: A faulty crankshaft sensor should be replaced promptly to prevent engine misfires or failure to start. Replacing this sensor often involves removing components like the timing belt or wheel for accessibility.
In summary, the crankshaft sensor is vital for the vehicle's engine management system, and its proper functioning is essential for optimal engine performance.
Detailed link:
050906433